Table of Contents
SAP Finance
In this article and the following articles we will run through various SAP Finance
configuration steps in detail. We will be configuring a Model Company in SAP. We will
configure and test below areas :
- Enterprise structure in sap
- SAP Finance Global Settings
- General Ledger
- SAP New GL
- Foreign Currency
- Inter-company posting
- SAP Special GL Transactions
- Validations & Substitutions in SAP
Enterprise Structure in sap
Localize
Global company code 0001 setting: O035
SAP supplied sample company code is
0001. This is country independent. So if the implementation is for USA this is localize
for country US installation. This is
than copied to the new organization units. This will copy below settings for
country installation:
- Chart of accounts
- Account determination
- Tax procedures
- Payment Methods
Path : SPRO – Enterprise Structure
• Localize Sample Organizational Units
Transaction code: O035
This will make settings of company
code 0001 as US in this case

Define Group Company
Company: A Company represents a group
company. The definition of company is optional.
A company can have one or more company
codes beneath it. Independent Financial Statements can be prepared for these
company codes.
All company codes with the same Company
must use the same operative Chart of
Accounts and Fiscal Year variant
Key
Fields
- Country : Specify the country where the company
is operating - Currency : This is local currency of the
company. All transactions for the Company are recorded in this currency only
SPRO Path : Enterprise Structure –
Definition – Financial Accounting -Define Company
Transaction code : OX15
Table: T880
Data:
| Company | Name | Country | Currency |
| MK1000 | MK Group of Companies | USA | USD |

Define Company code
Organization unit or Legal entity for
which independent financial statements can be prepared
Company code can be created from
scratch or from copying an existing company code
Company code 0001 is already defined
in clients 000 and 001 for the country DE (Germany).
All country-specific information
(parameters) that is typical for this country (including payment methods, tax
calculation procedures, and chart of accounts) is preset for this company code.
If, for example, you want to create a
company code for the United States to meet its legal requirements, you must
first run the country installation program (Transaction code :O035) in client
001 so that all the country-specific parameters are set to US
Table for Company code data: T001
Transaction Code : OX02
SPRO Path : SPRO – Enterprise
Structure – Definition – Financial Accounting – Edit
Company Code Data
Create company code from scratch
Transaction code: OX02
Data
| Co. Code | Country | Currency |
| MK14 | USA | USD |
Currency: Local currency of the
company code

Create company code by Copying Company code from an
Existing company code
Transaction code: EC01
Use this option when the SAP standard
company code 0001 has been localized. Copy from company code 0001
Create company code MK11 by copying
from company code 0001

Assign Company code to Group Company
SPRO Path : SPRO – Enterprise
Structure – Assignment – Financial Accounting – Assign Company Code To Company
Transaction code: OX16
Data: MK14 to MK1000

- Credit Control Area: A method of controlling
credit provided to customers - Credit control area is created below client
- One Credit control area can have one or more
company codes assigned to it - One Company code can be assigned to only one
Credit Control Area - Credit limits are assigned both in Customer
Master and Credit Control Area. At the time of credit check lower of the two is
considered - Credit Update Group: Can leave blank. Only AR
balance consider while calculating Credit limit for a customer. - All Company code : If selected posting from any
company code can be made to this Credit Control Area
Transaction code: OB45
Path : SPRO – Enterprise Structure –
Definition – Financial Accounting – Define Credit Control Area

Data
| Credit Control Area | Co. Codes | Limit | Currency |
| MK14 | MK14 | 50000 | USD |
Assign Company code to Credit Control area
Transaction code: OB38
Path : Enterprise Structure –
Assignment – Financial Accounting – Assign Company Code To Credit Control Area

Define Segments
- Segment is another account assignment object
- A Segment can be a Product, Department or a
Geographical location. Segment Reporting requires reporting Profit and Loss as
per segments. According to IAS, a business segment is a component of an entity
that provides a single product or service or a group of related products and
services and that is subject to risks and returns that are different from those
of other business segments - Segment reporting is required as per GAAP, IFRS, IAS
- Can create BS and P/L account for each segment
- Steps:
- Define segment
- Derive segment by assigning to Profit center in
the master data. Alternatively use BADI FAL_DERIVE_SEGMENT to derive segment. - Enable Segment field in Additional Account
assignment - Define Segment scenarios in New GL
SPRO Path : SPRO- Enterprise
Structure – Definition – Financial Accounting – Define Segment.
| Segments | Description |
| Seg A | Television Systems |
| Seg B | Refrigerators Systems |
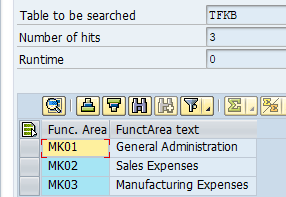
Define Functional area
Functional areas in an organization
are used to meet the cost of sales accounting requirements because they enable
you to classify the expenses by functions such as administration, sales,
marketing, and production. This is Cost of Sales Accounting
Functional area are assigned to GL
Accounts in transaction FS00 or for mass update transaction#OB_GLACC11
Path : Enterprise Structure –
Definition – Financial Accounting – Define Functional Area
Transaction code: FM_Function
SAP Finance Global Settings
SAP Finance Global settings performed in below Finance areas:
- Maintain Fiscal Year Variant
- Assign Company code to fiscal year variant
- Define Variant for Open posting period
- Assign Posting Period variant to Company code
- Open and Close Posting period
- Define Field Status variant
- Assign company code to field status variant
- Create Chart of Accounts
- Assign Company code to Chart of Accounts
- Define Account Groups
- Define Retained Earnings Account
- Define Account Type
- Define Document Number Range
- Define Posting Keys
- Change Message Type
- Tolerance
- Define Controlling area
Maintain Fiscal Year variant
- Fiscal Year means accounting year. An accounting year is a period of 12 months
- The fiscal Year may be a calendar year ( Jan to December).
- Fiscal Year variant can be non-Calendar year. A non-calendar year fiscal year variant contains 12 months starting from any month and ending in next year, one month before the start month. For e.g. period 1 is April and end on 31st March. Also it can begin from 15th April and end 14th April
- Yearend closing may require adjustment accounting entries which could be required to be posted in month after last period. To allow for these posting SAP allows for 4 special periods. Thus a Fiscal Year variant can have maximum of 16 periods with 4 special periods. The special postings are a part of the last posting period
Table of a Non Calendar Fiscal Year
| Cal Yr. | Cal Month | Fiscal Yr. | Posting Pd. | Start Dt. | End Dt. | Yr. Shift |
| 2014 | 4 | 2014 | 1 | 1 Apr | 0 | |
| 2014 | 5 | 2014 | 2 | 1 May | 0 | |
| 2014 | 6 | 2014 | 3 | 1 Jun | 0 | |
| 2014 | 7 | 2014 | 4 | 1 Jul | 0 | |
| 2014 | 8 | 2014 | 5 | 1 Aug | 0 | |
| 2014 | 9 | 2014 | 6 | 1 Sept | 0 | |
| 2014 | 10 | 2014 | 7 | 1 Oct | 0 | |
| 2014 | 11 | 2014 | 8 | 1 Nov | 0 | |
| 2014 | 12 | 2014 | 9 | 1 Dec | 0 | |
| 2015 | 1 | 2014 | 10 | 1 Jan | -1 | |
| 2015 | 2 | 2014 | 11 | 1 Feb | -1 | |
| 2015 | 3 | 2014 | 12 | 1 Mar | -1 |
SPRO Path : Financial Accounting (New) – Financial Accounting Global Settings (New) – Ledgers -Fiscal Year And Posting Periods – Maintain Fiscal Year Variant
Transaction code: OB29
- Specify Year dependent / Year Independent FYV
- Specify Number of posting periods and no. of special periods
- Specify calendar month for each posting period
- Specify end date of each period
- Specify Year Shift ( , -1, +1)
- Fiscal Year Variant K4 : It has calendar Fiscal year. Posting periods are equal to calendar months

FYV V3 = Non Calendar Year = Posting periods not equal to Calendar Months


Assign Company code to Fiscal Year Variant
SPRO Path : Financial Accounting (New) – Financial Accounting Global Settings (New) – Ledgers – Fiscal Year And Posting Periods – Assign Company Code To A Fiscal Year Variant
Transaction Code: OB37

Define Posting Period Variant
The benefit of defining variants to open periods is to avoid the problem of posting accounting transactions to the wrong period. This is achieved by opening current periods and closing all other periods. At the end of the current period, the period is closed and the next period is opened.
In SAP ERP, opening and closing periods are differentiated by account types. This allows you to determine which accounts are posted to a specific posting period. For example, posting can be permitted for accounts payable but not to accounts receivable.
As part of customizing opening and closing periods, the following items are defined:
- Define variants for open posting periods
- Assign variants to company codes
- Specify open and close posting periods
IMG Path : SPRO – Financial Accounting (New) – Financial Accounting Global Settings
(New) – Ledgers – Fiscal Year And Posting Periods – Posting Periods – Define Variants For Open Posting Periods
Transaction Code : OBBO

Assign Posting Period Variant to Company Code
IMG Path : SPRO – Financial Accounting (New) – Financial Accounting
Global Settings (New) – Ledgers – Fiscal Year And Posting Periods – Posting
Periods – Assign Variants To Company Code
Transaction Code : OBBP

Open and Close Posting period
- Copy SAP Standard Variant 0001
- Period 1: For posting to regular posting period
- Period 2: For posting to Special Periods. Periods 13 to 16 represent the special periods of four months for posting year-end adjustments to a closed fiscal year.
- For each interval specify
- Lower limit of interval
- Upper limit of interval
- Fiscal Year
IMG Path : SPRO – Accounting (New) – Financial Accounting Global Settings (New) – Ledgers –
Fiscal Year And Posting Periods – Posting Periods – Open And Close Posting Periods
Transaction code: OB52

Variant : Enter posting period variant like MK14 here
Column ‘A’: Enter the account type like A, D, K, S. + in first row is required to open the posting period variant
From Account : Lower limit of accounts. Can be left blank
To Accounts : Upper limit of accounts. Enter zzzzzzzzzz to include both numeric and non-numeric account number
From Period 1 : Enter the period to be opened
Year : Enter the year for From period which has to be opened
To Period 1 : Enter the period in relation to From period which have to be opened. For e.g if 12 is entered here and 1 in From period all period from 1-12 are open
Year : This is year corresponding to period specified in last step. So in above case period 1-12 are open from year 2019 to 2019
From Period 2 : From period for special periods. Enter 13 here
Year : Year corresponding to from special period
To Period 2 : Denotes end of special period. Enter 16 here
Year : Correspond to special period ‘To Period’.
Define Field Status Variant
Field status variants hold the Field Status Groups in SAP R/3. A Field Status Group defines the screen layout for a general ledger account entry. Based on your specification, the Field Status Groups determine which fields accept input during document entry (FB60, FB50, FB65…), as well as whether a field should be suppressed, required, and optional.
Define Field Status variant
Field status variant is made up of Field status group. In standard SAP Field status variant -0001 there are 42 FSG. These Field status group are assigned to GL account in FS00 to control their fields during document entry (FB60, FB70, F-02, and FB50)
Each Field status group is further made up of sub groups like General data, additional account assignment, Payment transactions etc.
Each of these sub groups have fields under them. These fields can be selected for states of Required/Optional/ Suppressed
IMG Path : SPRO- Financial Accounting (New) – Financial Accounting Global Settings (New) – Ledgers – Fields – Define Field Status Variants
Transaction Code : OBC4




Assign Company code to Field Status Variant
IMG Path : SPRO – Financial Accounting (New) – Financial Accounting Global Settings (New) – Ledgers – Fields Assign Company Code To Field Status Variants
Transaction Code : OBC5
Create Chart of Accounts
- Chart of Accounts contains the list of general ledger (G/L) accounts used by a company code for posting daily financial activities. Three types of COA
- SAP comes is delivered with country specific Chart of Accounts, Like CAUS for USA, CAGB for UK etc. COA INT is international COA and can be used for any country
- Operative: Used to record day to day financial transactions. Each company code must be assigned one Operative COA. One Operative COA can be assigned to many company codes
- Country: Maintained in addition to Operative COA. Link is established by entering GL account from country COA in alternative field in Operative COA
- Group: Contains the corporate G/L accounts applicable to all company codes in the group. It’s purely for consolidation reporting for the group. Link is established by entering Group GL account in the field Group GL in Operative COA. It is optional to maintain Group Chart of accounts
Create Chart of Accounts
We will create Chart of accounts MKUS for US company codes code MK14. However for US company codes MK11, MK12 we will use SAP supplied standard Chart of accounts for USA, which is CAUS.
For consolidation we will use SAP supplied standard chart of accounts CONS.
- Operative Chart of accounts for company code MK11, MK12, MK13 will be CAUS
- Country chart of accounts for MK13 will be MKSG
- Consolidation Chart of accounts for all company codes will be CAUS
IMG Path : SPRO – Financial Accounting (New) – General Ledger Accounting (New) –
Master Data – G/L Accounts – Preparations – Edit Chart Of Accounts List
Transaction code: OB13

Assign Company code to Chart of Accounts
Transaction code: OB62

Define Account Group
- Accounts are classified into appropriate account groups by grouping accounts with similar tasks together in the same general ledger. For example, all G/L accounts related to revenue are grouped together under Revenue Group and assigned the same number range
- Account Group control General Ledger account number
- Fields displayed for a GL Account in FS00 (GL Master Data)
IMG Path : SPRO – Financial Accounting (New) – General Ledger Accounting
(New) – Master Data – G/L Accounts – Preparations – Define Account Group
Transaction Code : OBD4

Define Retained Earnings Account
Normally, the net profit or net loss figure is carried forward to retained earnings on the balance sheet.
Retained earnings account defined here needs to be created in FS00. At the end of fiscal year balance in Profit and Loss is c/f to RE accounts
IMG Path : SPRO – Financial Accounting (New) – General Ledger
Accounting (New) – Master Data – G/L Accounts – Preparations – Define
Retained Earnings Account
Transaction code: OB53

Define Document Type
FI Document
Every posting in the SAP system generates a document, and the document remains open until it is cleared and archived. For example, when an invoice is posted in the system, the system generates a document and assigns a document number. The invoice remains in the system as an open item. When payment is received for the invoice, the amount received is entered into the system and cleared with the outstanding invoice. A document is uniquely identified using:
- Document number: This is a unique number that is assigned to a document automatically by the system during document posting or manually by the user during data input.
- Company code: This is your company’s identification code.
- Fiscal year: This is your company’s accounting year code. This is usually a 12-month period.
A document has two main components. Header and Line Items. Header is made up of below fields
- Document Date: This is the original document / vendor invoice date
- Posting date: Date on which document is accounted in the GL account
- Document Type: This determine the type of accounts (S, K, D,A) to which the document can be posted. It also control the field status of the document during entry
- Company code: Legal entity to which the transaction belongs
- Currency/ Exchange rate: If the document currency is different from company code currency system uses the exchange rate configured in the system. If we want a different rate to be used specify the rate in this field
- Translation date: If system has to use an exchange which is different from the document date enter the date in this field
- Period: This is derived from posting date. Documents can be posted only in open posting periods. Typically period is the month in which a document is posted. However a document can be posted in period 14 (special period) with a posting date of Dec 10, 2018 (Fiscal year = Calendar Year)
- Reference: Generally external document number is entered here. Can be made mandatory in document type configuration
Following entries are made automatically by the SAP at the time of document posting
- Tax amount on sale / purchase of customer / vendor invoice based on tax rate entered
- Payables and receivable between company codes in case of intercompany transactions
- Gain / loss due to exchange rate difference
- Cash discount paid / received during vendor payments (F110)
Define Document Type
IMG Path : SPRO – Financial Accounting (New) – Financial Accounting Global Settings (New) – Document – Document Types – Define Document Types
Transaction code: OBA7
This is a two-character key which distinguishes the business transaction to be posted, such as vendor invoice, customer invoice, vendor invoice payment, and so on.
- Defined at client level
- Control type of Account that can be posted with the document type
- S: GL Accounts
- K: Vendor Accounts
- D: Customer Accounts
- A: Assets Accounts
- M: Materials
- Control the number range that can be used by this document type
- Can make Reference and Text field mandatory for this document type
- If exchange rate type is specified, uses the exchange rate as per the exchange rate type specified here in case no exchange rate is entered during document entry
- Negative posting’s permitted: If this field is selected document type can be used for negative reversal postings.
- Trading Partner: If this field is selected trading partner has to be entered manually in document. Generally trading partner is transferred from customer / vendor master records automatically
- Reference / Doc header text: If selected, the field is made mandatory in the document

Define Document Number Range
- Document Number Ranges are company code dependent so need to be created for each company code
- Document number range can be internal or external
- Year Independent: Valid for all year till year 9999. Enter year 9999 in FBN1
- Year Dependent: Valid for specific year. Enter the specific year in FBN1
- Create separate number range for special document types like recurring documents. SAP recommends using the number range interval X1 for recurring entry documents and X2 for sample documents in order not to interfere with SAP’s standard settings
IMG Path : SPRO – Financial Accounting (New) – Financial Accounting Global Settings (New) – Document – Document Number Ranges – Documents In Entry View – Define Document Number Ranges
Transaction code: FBN1

To copy number range from company code use transaction OBH1
To copy number range from another fiscal year use transaction : OBH2
Define what fields can be changed in a Document header
Specify the fields which can be changed in a document for account types (S, A, D, K)
IMG Path : SPRO – Financial Accounting (New) – Financial Accounting Global Settings
(New) – Document – Rules For Changing Documents – Document Change Rules
Transaction code: OB32

Define Posting Keys
Transaction code: OB41
PK controls the processing of line items in a document. It controls the following:
- DR / CR entry
- Account Type (D, K, S, A, M)
- Field status of the document entry screen
It is recommend to use the SAP provided posting keys

Change Message type displayed during document processing
IMG Path : SPRO – Financial Accounting (New) – Financial Accounting Global Settings – Document – Default Values – Change Message Control For Document Processing
Transaction code OBA5
Select Area F5, F5A for document processing
FI Accounting Area: FF

Tolerances
For example, an outstanding invoice amount is $5000 and the amount paid to clear the outstanding invoice is $4950, leaving you with a difference of $50. If the acceptable limit for your tolerance groups is $45, the system will reject the posting because the difference is above the acceptable limit. On the other hand, if the payment difference is $45 or less, the system will accept your posting and post the difference to a specified predefined account.
Three tolerances are represented in SAP ERP.
- Tolerance groups for G/L accounts
- Tolerance groups for employees
- Tolerances for customers/vendors
Tolerance groups for G/L accounts : Define the limits within which credit and debit differences in local currencies are considered acceptable. The differences are posted automatically during G/L account clearing.
Define Tolerance Group for GL account tolerances : OBA0

Tolerance Group for Employees: OBA4
Define what an employee is permitted to post to the system.

- Amount per Document: This is the maximum amount per document an employee is authorized to post.
- Amount per Open Item Account Item: This is the maximum amount per open item that the employee can enter in the line item in a vendor/customer account.
- Cash Discount per Line Item: This is the maximum cash percentage discount per line item that the employee can grant.
- Permitted Payment Differences : During payment difference posting, the system will check the amount against the percentage and automatically use whichever is less.
Tolerance Group for Vendors: OBA3
Driving entries to Cash discount account, Over / Under Payment account during payment to Vendors. These vendor tolerances are assigned to vendor master. When payment are made to the vendor. Differences between invoices and payment received if within the limit defined here, than posted automatically to GL accounts defined earlier. Null tolerance group is assigned automatically to all vendors master. Non Null Tolerance Group has to be assigned in the vendor master

Enter Company Code Global parameters
Transaction Code: OBY6
IMG Path : Financial Accounting (New) – Financial Accounting Global Settings (New) – Global Parameters For Company Code – Enter Global Parameters
- Country COA: Enter if different from Operative COA
- External Company code: Selected in case of ALE entries coming from a different SAP system.
- Global company code: In conjunction with external company code enter the external system Sending/ Receiving ID
- Workflow variant : Use transaction OBWA to create workflow variant BSUS and assign to company code BS11
- Negative Postings : select. Allowed as to not inflate the trial balance
- Activate Cash Management : Select to activate cash management and liquidity forecast
- No Forex Rate Diff. when Clearing in LC: Use this box to control how foreign currency open items are cleared in local currency. When you select this checkbox, the system clears the foreign currency open items using the prevailing exchange rate when those open items were created.
- Tax Base is Net Value : If selected discount deducted from Invoice value and tax is calculated on this net amount

For detailed, step-by-step instructions on SAP Finance Business process, configuration and development follow along with my video tutorial below.
Define Controlling area
Transaction code: OKKP
IMG Path : SPRO – Enterprise Structure – Definition – Controlling – Maintain Controlling Area
- Like a company code, it is a self-contained cost accounting entity useful for internal reporting.
- You can have one or more controlling areas in a single client. You assign one or
- more controlling areas to an operating concern.
- An operating Concern can have one or more controlling areas
- One or more company codes can be assigned to a Controlling Area
- All Company codes assigned to a Controlling Area must use the same Chart of Accounts
- Controlling Area ensure that primary expenses from FI are posted to cost objects (Cost center, Internal Order, WBS) in CO. Similarly revenue from FI are posted to CO-PA and Profit Center accounting in Controlling
Controlling area field explained:
- Currency Type
- 10 – Local / Company code currency
- 20 – Controlling area currency. This can be any currency
- 30 – Group currency. This is the Client level currency Type
- Cocd->CO Area: Multiple company codes can be assigned to a controlling area. All company codes must use the same Fiscal Year Variant
- Chart of Accounts : Ensure all company codes assigned to the controlling area use same operative Chart of accounts. Can have different country chart of accounts

Assign Controlling Area to Company code

Activate Controlling Area Components
Transaction code : OKKP
Select and activate below components in the controlling area.

For detailed, step-by-step instructions on SAP Finance, business process, configuration and development follow along with my video tutorial below. This course covers topics like Enterprise structure, General Ledger, Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable, Bank Accounting, Electronic Bank statements, Dunning, New General Ledger etc.

Pingback: SAP Finance Global Settings - SAP FINANCE and Treasury
Pingback: SAP Inter-company code Transactions |
Pingback: SAP Special GL Transactions |
Pingback: SAP Finance Validations |
Pingback: SAP Finance Substitutions |
Pingback: Vendor Payments Business process, Configuration and testing in SAP |
Pingback: Vendor Payments-ACH/Wire, DMEE-Part 2 | SAP FINANCE and Treasury
Pingback: SAP Controlling Overview | SAP FINANCE and Treasury
Pingback: SAP iDoc Part 3 | Create extended iDoc | Add segments to iDoc
Pingback: SAP Cost Center Accounting-2 | SAP FINANCE and Treasury
Pingback: SAP Cost Center Accounting-3 (Report Painter) | SAP FINANCE and Treasury
Pingback: SAP Internal Order | SAP FINANCE and Treasury
Pingback: SAP Cash position report
Pingback: SAP Profit Center Accounting | SAP FINANCE and Treasury
Pingback: sap electronic bank statement
Pingback: SAP Treasury and Risk Management | Money Market instruments
Pingback: SAP accounts receivable | Dunning
Pingback: SAP Cost Center | SAP FINANCE and Treasury
Pingback: SAP Asset Accounting Business Process | SAP FINANCE and Treasury
Pingback: SAP AP Master Data
Pingback: SAP Tables | SAP FINANCE and Treasury
Pingback: SAP FI-MM Integration | SAP FINANCE and Treasury
Pingback: SAP-Electronic Bank Statement Tutorial 2 | SAP FINANCE and Treasury
Pingback: SAP AR Master Data | SAP FINANCE and Treasury
Pingback: SAP Finance Tutorials | AUMTECH Solutions-SAP Training
Pingback: SAP S4/HANA Finance Part-1 | AUMTECH Solutions-SAP Training
Pingback: SAP FICO Interview Questions & Answers | AUMTECH Solutions-SAP Training